INTRODUCTION
We are from KT1T1a have been given a project to make a blog about Biodiversity, Kingdom Animalia.
 |
| THE STRUCTURE OF KINGDOM ANIMALIA |
Objectives
At the end of this topic, students should be able to:
a)Describe the uniques characteristics of Kingdom Animalia
b)State the classification of Animalia into 9 phyla:
-Phylum Porifera
-Phylum Coelenterata/Cnidaria
-Phylum Platyhelminthes
-Phylum Nematoda
-Phylum Annelida
-Phylum Arthropoda
-Phylum Mollusca
-Phylum Echinodermata
-Phylum Chordata
Unique characteristics of Kingdom Animalia
-Eukaryote
-Multicellular
-Heterotrophic
-Store excess carbohydrates as glycogen
-Have differentiated tissue for response to stimuli and locomotion
-Reproduce sexually (most)
-Dominant stage in the life cycle is diploid
Phylum Porifera
Objectives
At the end of this topic, students should be able to:
-Describe the unique characteristics of Phylum Porifera, Euspongia sp.
Unique characteristics of Phylum Porifera
-Consists of all species of sponges
-No true tissues
-Asymmetrical
-No body cavity
-Most are sessile
-Aquatic mainly marine
-Body has an exoskeleton made upof spicules
-Reproduce secually and asexually
-Hermaphrodite (can produce both eggs and sperm)
-Water movement
.Enter (Ostium)
.Exit (Osculum)
-Feeding
.Flow of water through the sponge allow for feeding, waste removal and the intake of oxygen
.A combination of pressure, flagella and contractile movement pump water
Phylum Coelenterata/Cnidaria
Objectives
At the end if this topic, students should be able to:
a)Describe the unique characteristics of Phylum Cnidaria
b)State three common classes:
-Class Hydrozoa(hydra,Obelia sp.)
-Class Scyphozoa(jellyfish,Aurelia sp.)
-Class Anthozoa(sea anemone,Actinia sp.)
Unique characteristics of Phylum Cnidaria
-Tissue level
-Radial symmetry
-Diploblastic
-Tentacles(locomotion and food capturing)
-Cnidocyte or stinging cells in the tentacles(defense and capturing prey)
Classification of Phylum Cnidaria
-Class Hydrozoa(hydra,Obelia sp.)
-Class Scyphozoa(jellyfish,Aurelia sp.)
-Class Anthozoa(sea anemone,Actinia sp.)
Dimorphism/Polymorphism
-Kingdom Cnidaria have 2 basic body forms which are:
.Polyp
.Medusa
Polyp forms:
-Tubular body
-Mouth and tentacles are directed upward
-Small amount of mesoglia
-Sessile
Medusa forms:
-Bell-shaped body
-Mouth and tentacles are directed downward
-Large amount of mesoglia
-Motile
Life cycle of hydra, Obelia sp.
-Sexual reproduction involves the production of medusae which bud from the second type of polyp, called reproductive polyps
-They produce tiny free-swimming sexual medusae(male and female) complete with tentacles and gonads, which release eggs cells and sperms into the water
-Fertilization results in a zygote which develop to form planula larva consisting of a ball of cells with a ciliated outer layer
-Planula larva develop to produce new mature polyps
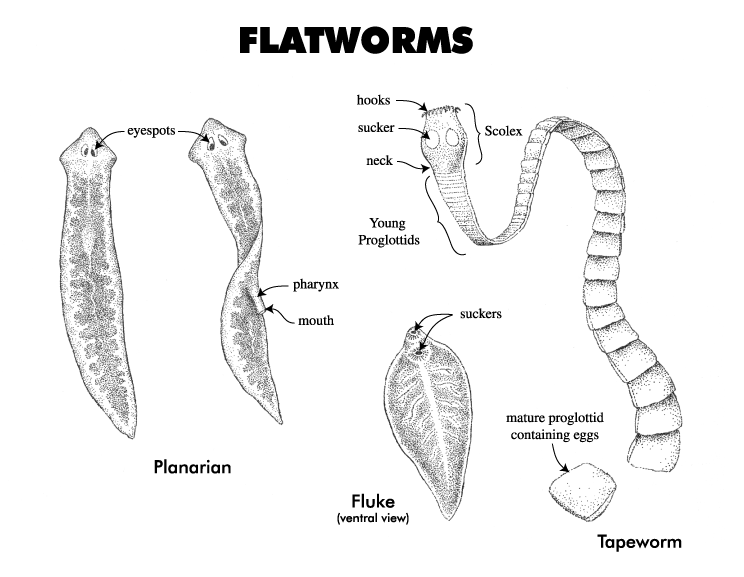
Phylum Platyhelminthes
Objectives
At the end of this topic, students should be able to:
a)Describe the unique characteristics of Phylum Platyhelminthes
b)State 3 common classes:
-Class Cestoda(tapeworm,Taenia sp.)
-Class Turbellaria(Dugesia sp.)
-ClassTrematoda(Fasciola sp.)
Unique characteristics of Phylum Platyhelminthes
-Organ level
-Bilateral symmetry
-Triploblastic
-Acoelomate
-Unsegmented
-Show cephalization
.Development of head region
-No specialized circulatory or respiratory structure
.Gas exchange occur by diffusion
-Incomplete digestive system
.Has mouth but no anus
-Excretory system
.Protonephridia
Phylum Nematoda
Objectives
At the end of this topic, students should be able to:
a)Describe the unique characteristics of Phylum Nematoda
Unique characteristics of Phylum Nematoda
-Elongated, smooth narrow cylindrical body with tapered tail and blunt head
-Organ system level
-Bilateral symmetry
-Triploblastic
-Pseudocoelomate
-Unsegmented
-Most are free living
.Found in fresh water, marine, moist soil
-Some are parasitic
-Complete alimentary canal
.with separate mouth and anus
-Nervous system
.Simple with several ganglia in the head region(but no brain)
.Nerves extend from ganglia that funtional to control movement
-Excretory system
.Has anus
.Excretory pore
-No circulatory and respiratory systems
-Have hydrostatic skeleton
.To maintain shape and allows for locomotion
-Reproduction
.Dioecious(separate sexes in most species)
.Internal fertilisation
-Body is covered with smooth cuticle
.Provides protection
.Reduce H20 loss
.withstand hydrostatic pressure of pseudocoelom
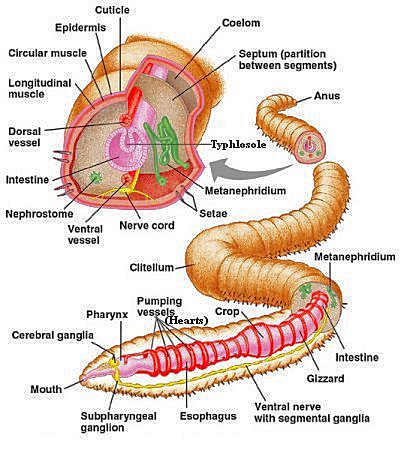
Phylum Annelida
Objectives
At the end of this topic, students should be able to:
a)Describe the unique characteristics of Phylum Annelida
b)State 3 common classes
-Class Olichaeta(earthworm,Pheretima sp.)
-Class Polychaeta(rag worm,Nereis sp.)
-Class Hirudinea(leech,Hirudo sp.)
Unique characteristics of Phylum Annelida
-Organ system level
-Bilateral symmetry
-Triploblastic
-Coelomate
-Metamaric segmented
.Division of body into a number if segments each contains same organs
-Coelomates
.Fluid-filled cavity between the gut and the other body organs
-Free-living, trrestrial or aquatic form
-Complete digestie system
-Excretory system
.Consists of a pair of metanephridium
-Closed body circulation system
-Respiratory system
.Through skin or gills
Chitinous setae
.Each segments have setae to assist movement
-Reproduction system
.Most reproduce sexually
.Dioecious or monoecious
Classification of Phylum Annelida
-Class Oligochaeta(earthworm,Pheretima sp.)
-Class Polychaeta(rag worm,Nereis sp.)
-Class Hirudinea(leech,Hirudo sp.)
Class Oligochaeta
-Oligo(few) + Chaeta(bristles)
-Bristles help in anchoring or burrowing
-earthwom,Pheretima sp.
Class Polychaeta
-Poly(many) + Chaeta(bristles)
-Paired-paddle-like appendages that are tip with bristles
-Sandworm,Nereis sp.
Class Hirudinea
-Have no setae
-Suckers for attaching to host
-Leech,Hirudo sp.
Roles of Phylum Annelida
-Soil aeration
-Medical use
Phylum Arthropoda
ObjectivesAt the end of this topic, students should be able to:
a)Describe the unique characteristics of Phylum Arthropoda
b)State the 6 common classes:
-Class Crustacea(Macrobrachium sp.)
-Class Chilopoda(Scolopendra sp.)
-Class Diplopoda(Julus sp.)
-Class Insecta(Valanga sp.)
-Class Arachnida(Nephila sp.)
-Class Merostomata(Tachypleus sp.)
Unique characteristics of Phylum Arthropoda
-Arthropoda means jointed legs
-Organ system level
-Bilateral system
-Triploblastic
-Hemocoel
-Segmented
-Cephalization
.Thorax is fused with the head to form Cephalothorax
-Digestion
.Complete digestive system
-Excretory system
-Nervous system
.a double cerebral ganglion
.a double ventral nerve cord network of nerves
-Exoskeleton
.Protective and mobile
-Movement
.segmentation and appendages
-Reproduction
.Reproduces sexually
-Respiration through
.Gill
.Trachea
.Book lungs
.Diffusion via skin
Contribution of the unique characteristics of Phylum Arthropoda
-Exoskeleton
.Supports and protects the body
-Segmentation and appendages
.appendages for better locomotion
-Antagonistic striated muscles
.Provide brisk movement
.Help to find foot, to breed and run out from predator
-Highly developed sensory organs
.Compund eyes, receptors for smell
-Reduced ompetition through metamorphosis
.Less interspecies competition
Classification of Phylum Arthropoda
-Class Crustacea(prawn,Macrobrachium sp.)
-Class Chilopoda(centipede,Scolopendra sp.)
-Class Diplopoda(Millipede,Julus sp.)
-Class Insecta(Grasshopper,Valanga sp.)
-Class Arachnida(Spider,Nephila sp.)
-Class Merostomata(Horseshoe crab,Tachypleus sp.)
Phylum Mollusca
Objectives
a)Describe the unique characteristics of Phylum Mollusca
b)State 3 common classes:
-Class Gastropoda(Achatina sp.)
-Class Chephalopoda(Sepia sp.)
-Class Bivalvia(Anadara sp.)
Unique characteristics of Phylum Mollusca
-Organ system level
-Assymmetry
-Triploblastic
-Unsegmented
-Coelomate
-Mollusca inhabits marine,freshwater and terrestrial habitats
-The Mollusca body plan includes:
.Visceral mass(Contain the internal organs)
.Muscular foot(For locomotion and attachment)
.Mantle(Have a gland that secrete the shell)
-Excretory system
.Nephridia
-Circulatory system
.Open/closed blood circulation
-Respiratory system
.Gills or lungs
-Advanced nervous system
.Brain
.Well developed sense organs
-Reproduction
.Monoecious and Dioecious
Classification of Phylum Mollusca
-Class Gastropoda(Achatina sp.)
-Class Chephalopoda(Sepia sp.)
-Class Bivalvia(Anadara sp.)
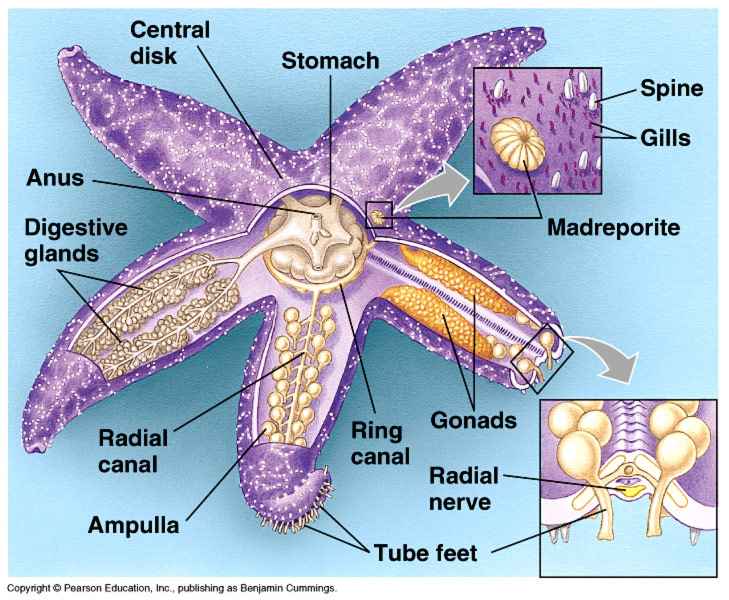
Phylum Echinodermata
Objectives
At the end of this topic, students should be able to:
a)Describe the unique characteristics of Phylum Echinodermata
b)State 3 common classes:
-Class Asteroidea(starfish,Asterias sp.)
-Class Holothuroidea(sea cucumber,Holothuria sp.)
-Class Enchinoidea(sea urchin,Diadema sp.)
Unique Characteristics of Phylum Echinodermata
-Organ system level
-Triploblastic
-Bilateral symmetry(larvae) / Radial symmetry(adult)
-Coelomate
-Habitats in aquatic
-No cirulatory, respiratory or excretory systems
-Sessile
-Endoskeleton
-Sexual reproduction / Asexual reproduction
Classification of Phylum Echinodermata
-Class Asteroidea(starfish,Asterias sp.)
-Class Holothuroidea(sea cucumber,Holothuria sp.)
-Class Echinoidea(sea urchin,Diadema sp.)
Phylum Chordata
Objectives
At the end of this topic, students should be able to:
a)Describe the unique characteristics of Phylum Chordata:
-Notochord
-Presence of Pharyngeal Cleft
-Dorsal hollow nerve cord
-Post anal tails
-Myotomes
b)State the classification of Phylum Chordata into 4 subphyla:
-Urochordata(Sea squirt)
-Hemichordata(Acorn worm)
-Cephalochordata(Lancelet)
-Vertebrates
c)State 6 common classes of sub-phlum Vertebrates:
-Class Chondrichthyes(cartilaginous fish,Raja sp.)
-Class Osteichthyes(bony fish, Selar sp.)
-Class Amphibia(frog,Rana sp.)
-Class Reptile(crocodile,Crocodilus sp.)
-Class Aves(pigeon,Columba sp.)
-Class Mammalia(rat,Rattus sp.)
Unique characteristics of Phylum Chordata
-Organ system level
-Triploblastic
-Coelomate
-Segmented
-Bilateral symmetry
-Complete digestive system
-Have brain
-Notochord
.Provides skeletal support
-Presence of Pharygeal Cleft
.Found in all chordate embryos
.Suspension feeding devices(Invertebrate chordates)
.Modified for gaseous exchange(Vertebrates)
-Dorsal hollow nerve cord
.Develops into central nervous system
.Brain and nerve cord
-Post anal tail
.Provides propelling force in many aquatic species
-Myotomes
.Muscular tissues arranged in blocks
-Close circulatory system
Classification of subphyla
-Subphylum Urochordata(sea squirt)
-Subphylum Hemichordata(Acorn worm)
-Subphylum Chephalochordata(Lancelet)
-Vertebrates
Classes of subphylum Vertebrates
-Class Chondrichthyes(cartilaginous fish,Raja sp.)
-Class Osteichthyes(bony fish,Selar sp.)
-Class Amphibia(frog,Rana sp.)
-Class Reptile(crocodile,Crocodilus sp.)
-Class Aves(pigeon,Columba sp.)
-Class Mammalia(rat,Rattus sp.)








Tiada ulasan:
Catat Ulasan